Trump’s Second Paris Agreement Exit (2025): Impact on Global Climate Policy
Understanding the Paris Climate Agreement
The Paris Climate Agreement is a legally binding international treaty focused on mitigating climate change through national commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Participating countries submit Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) that outline their specific goals for emission reduction, renewable energy adoption, and sustainability initiatives.
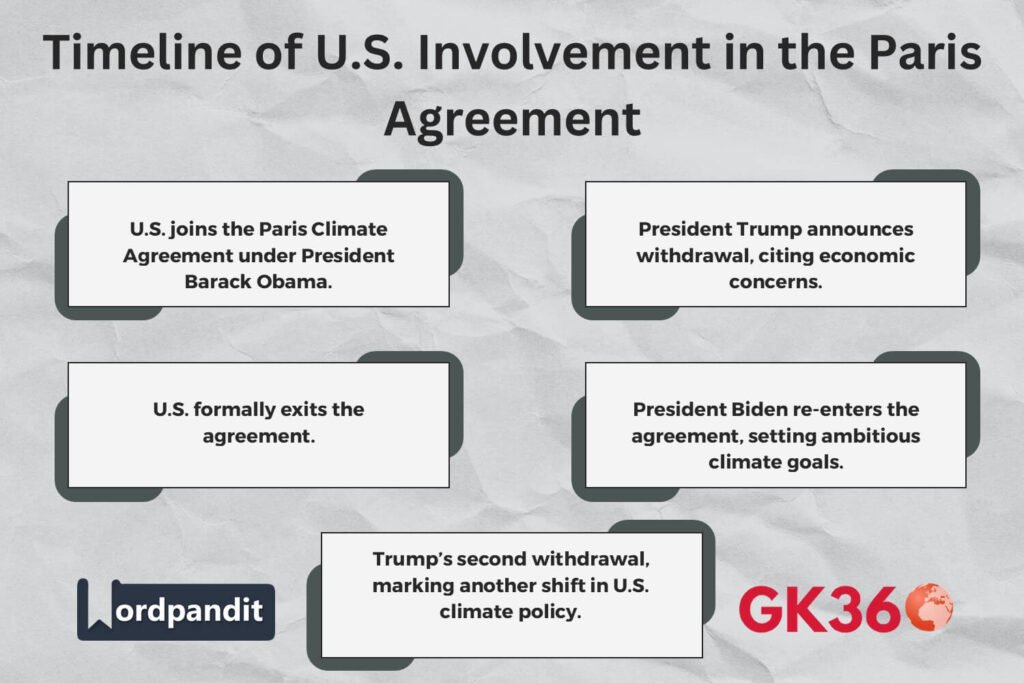
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Paris Climate Agreement
- Trump’s First Exit (2017) and Its Impact
- Biden’s Reinstatement (2021): A Shift Toward Climate Action
- Trump’s Second Exit in 2025: Reasons & Controversy
- Implications for Global Climate Efforts
- International Reactions & Diplomatic Fallout
- The US as a Major Emitter: Future Climate Responsibility
- Timeline of Withdrawal & Potential Re-entry Scenarios
- Broader Implications for Energy Policy and Global Cooperation
- FAQ Section
- Conclusion + Call-to-Action
Trump’s First Exit (2017) and Its Impact
In 2017, President Trump announced the U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, arguing that it imposed unfair economic burdens on the nation while allowing countries like China and India to benefit. This decision led to:
- A reduction in federal climate policies and funding.
- Backlash from environmental organizations and global leaders.
- A shift in U.S. climate leadership, with states and corporations independently committing to emission reductions.
Biden’s Reinstatement (2021): A Shift Toward Climate Action
Upon taking office in 2021, President Biden rejoined the Paris Agreement and introduced aggressive climate policies, including:
- A pledge to reduce U.S. greenhouse gas emissions by over 60% by 2035.
- Increased investment in renewable energy and electric vehicle infrastructure.
- International collaboration on climate resilience initiatives.
Trump’s Second Exit in 2025: Reasons & Controversy
On January 20, 2025, during his second term, Trump signed an executive order withdrawing the U.S. from the Paris Agreement again. His reasoning included:
- Economic concerns, claiming the agreement hurt American industries.
- Sovereignty arguments, stating that international agreements should not dictate U.S. policy.
- Allegations of global bias against the U.S., favoring developing nations.
This move positioned the U.S. alongside countries like Iran and Libya, the only other nations not participating in the agreement.
Implications for Global Climate Efforts
The withdrawal has far-reaching consequences, as the U.S. is the second-largest emitter of greenhouse gases. Experts warn that:
- The decision could weaken global momentum toward climate action.
- Other countries might scale back their commitments.
- It may lead to increased risks of extreme weather events and rising sea levels.
International Reactions & Diplomatic Fallout
Global leaders condemned the decision, with EU President Ursula von der Leyen reaffirming Europe’s commitment to climate goals. United Nations climate chief Simon Stiell emphasized the irreversible momentum of renewable energy and climate policies worldwide, regardless of U.S. participation.
The US as a Major Emitter: Future Climate Responsibility
As one of the world’s top polluters, the U.S. plays a crucial role in reducing emissions. Without federal participation, progress now relies on:
- State-led climate initiatives.
- Corporate sustainability commitments.
- Technological advancements in clean energy.
Timeline of Withdrawal & Potential Re-entry Scenarios
The formal U.S. withdrawal process takes one year, meaning it will be official by early 2026. However, future administrations could rejoin under new terms.
Broader Implications for Energy Policy and Global Cooperation
- Economic Impact: Potential loss of clean energy investments.
- Trade Relations: Strained ties with climate-focused nations.
- Scientific Innovation: Potential slowdown in research funding.

FAQ Section
- Why did Trump withdraw from the Paris Agreement again in 2025? Trump cited economic disadvantages and concerns over national sovereignty.
- How will this impact the U.S. economy? The withdrawal may boost fossil fuel industries but could harm renewable energy investments and international trade relations.
- What are the global consequences of this decision? Reduced U.S. leadership in climate initiatives may slow global progress and weaken emissions reduction targets.
- Could the U.S. rejoin the Paris Agreement in the future? Yes, a future administration could reinstate U.S. participation, as seen with Biden in 2021.
- How does this affect U.S. climate policies at the state level? Many U.S. states and corporations will likely continue climate initiatives independent of federal policies.
Conclusion
Trump’s second withdrawal from the Paris Agreement in 2025 marks a pivotal moment in climate diplomacy. While the decision creates challenges for global climate efforts, state governments, businesses, and international organizations continue to drive progress in sustainability.
Key Takeaways Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Paris Agreement Goal | Limit global warming below 2°C, with a target of 1.5°C. |
| Trump’s 2017 Exit | Cited economic disadvantages & sovereignty concerns. |
| Biden’s 2021 Reentry | Set ambitious greenhouse gas reduction targets & clean energy funding. |
| Trump’s 2025 Exit | Announced citing economic burdens, bias against U.S., and fossil fuel industry protection. |
| Global Reactions | EU & UN condemn withdrawal, China & India reaffirm climate commitments. |
| Economic Impact | Potential loss of clean energy investments & strained trade relations. |
| Future Re-entry Possibilities | A new administration could rejoin, similar to Biden’s 2021 move. |
Related terms
- Trump Paris Agreement Exit 2025
- U.S. Climate Policy Reversal
- Paris Climate Agreement Withdrawal
- Global Warming & U.S. Policy
- Renewable Energy vs Fossil Fuels
- Climate Change & International Diplomacy
- Trump’s Climate Legacy
- U.S. and Global Carbon Emissions
- Future of U.S. Environmental Policy
- Biden vs Trump Climate Strategies





