NITI Aayog: A Decade of Transforming India’s Governance Framework
Introduction
NITI Aayog emerged as a pivotal reform in India’s governance, replacing the erstwhile Planning Commission. Announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his Independence Day speech in 2014, the institution was envisioned as a modern and dynamic entity. NITI Aayog’s design emphasized decentralization, competitive federalism, and inclusive growth, setting it apart from its predecessor. Over the last decade, it has evolved as a hub of policy innovation and collaboration, addressing India’s complex developmental challenges.
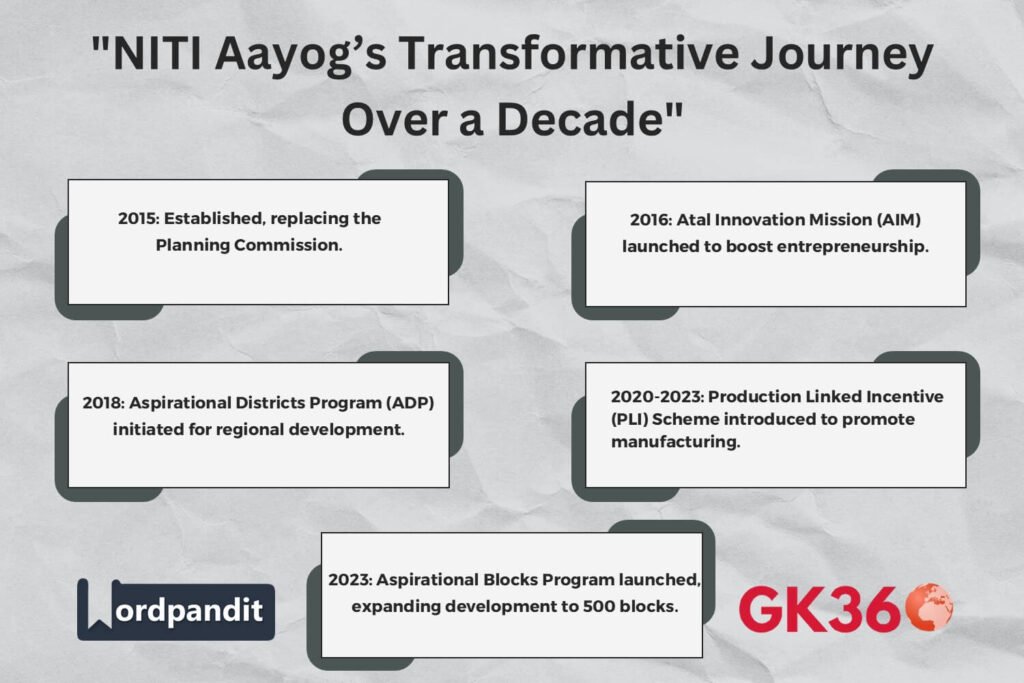
Table of Contents
- Key Insights and Achievements of NITI Aayog’s First Decade
- Key Initiatives and Their Impact
- Partnership with States and Local Governments
- Challenges and Future Directions
- Goals for 2030
- Vision for 2035
- About NITI Aayog
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
Key Insights and Achievements of NITI Aayog’s First Decade
Decentralization and Competitive Federalism
- NITI Aayog heralded a transformative shift in governance by decentralizing power.
- Unlike the highly centralized Planning Commission, it promotes cooperative and competitive federalism.
- Introduction of data-driven indices such as:
- SDG India Index
- Composite Water Management Index
- Encourages state-led governance while ensuring accountability at every level.
Limited Union-Level Involvement
- Functions as an advisory and coordinating body rather than an implementing agency.
- Collaborates with Union ministries but does not control financial allocations.
- Enhances inter-ministerial coordination to address policy challenges.
Key Initiatives and Their Impact
Aspirational District Program (2018)
- Focuses on transforming 112 underdeveloped districts.
- Targets health, education, agriculture, and infrastructure.
- Implements monthly performance evaluations to incentivize local governance.
Aspirational Block Program (2023)
- Expands the Aspirational District Program to 500 blocks.
- Ensures comprehensive implementation of government schemes at the block level.
Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) (2016)
- Promotes innovation and entrepreneurship.
- Includes Atal Tinkering Labs and Atal Incubation Centres.
- AIM 2.0 focuses on expanding innovation in Jammu & Kashmir and the Northeast.
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme
- Encourages domestic manufacturing and job creation.
- Focus sectors: electronics, textiles, automobiles.
- Aims to enhance India’s self-reliance and industrial growth.
Partnership with States and Local Governments
- As a politically neutral institution, NITI Aayog fosters cooperative federalism.
- Annual meetings with Chief Ministers and Chief Secretaries to align development priorities.
- Implements the “Team India” concept for unified growth.
Data-Driven Governance
- SDG India Index and Composite Water Management Index track national and state performance.
- Uses data analytics to promote transparency and targeted interventions.
Technological Innovation for Employment
- AIM and PLI initiatives leverage technology to create jobs and enhance productivity.
Challenges and Future Directions
Cross-Departmental Coordination
- Need for seamless collaboration among central ministries and state governments.
- Aligning short-term and long-term national priorities.
Climate and Sustainability Goals
- NITI Aayog must integrate sustainability into its developmental agenda.
- Aligning India’s policies with global climate commitments.
Youth Employment and Skill Development
- Addressing unemployment through skilling programs and technological advancement.
- Preparing India’s workforce for a dynamic job market.
Goals for 2030
- Energy Transition
- 50% of energy from renewable sources.
- Achieving 500 GW non-fossil energy capacity.
- Reducing carbon emissions by one billion tonnes.
- Public Health
- Strengthening surveillance systems for non-communicable diseases.
- Addressing environmental health issues.
Vision for 2035
- Sustained Economic Growth: Balancing economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability.
- Energy Security: Providing affordable, accessible, and secure energy.
- AI Integration: Implementing Artificial Intelligence in healthcare, education, agriculture, and urban planning.
About NITI Aayog
Structure and Composition
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India.
- Executive Leadership: Vice-Chairperson and CEO.
- Governing Council: Includes Chief Ministers, Lieutenant Governors, Vice Chairperson, and full-time members.
Core Roles
- Policy Formulation and Strategic Advice
- Promoting Cooperative Federalism
- Monitoring and Evaluation of Programs
- Fostering Innovation and Research
- Advancing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q1: What is NITI Aayog, and why was it formed?
A: NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) was established on January 1, 2015, replacing the Planning Commission. It was formed to promote decentralized governance, cooperative federalism, and evidence-based policymaking. - Q2: How is NITI Aayog different from the Planning Commission?
A: Unlike the Planning Commission, which controlled financial allocations, NITI Aayog functions as an advisory and coordinating body. It emphasizes cooperative federalism, state participation, and data-driven policymaking. - Q3: What are some key initiatives launched by NITI Aayog?
A: Major initiatives include:- Aspirational Districts Program (ADP) – Transforming 112 underdeveloped districts.
- Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) – Promoting entrepreneurship and start-ups.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme – Boosting domestic manufacturing.
- SDG India Index – Tracking India’s progress on Sustainable Development Goals.
- Aspirational Blocks Program – Extending ADP’s success to 500 blocks.
- Q4: How does NITI Aayog promote cooperative federalism?
A: NITI Aayog works closely with states and local governments through:- Annual meetings with Chief Ministers and Chief Secretaries.
- Developing state-specific policy recommendations.
- Encouraging states to compete in key areas via performance indices.
- Q5: What is the Aspirational Districts Program, and why is it important?
A: Launched in 2018, the Aspirational Districts Program (ADP) aims to uplift 112 of India’s most backward districts by improving health, education, agriculture, and infrastructure through data-driven performance monitoring. - Q6: What role does NITI Aayog play in India’s economic growth?
A: NITI Aayog provides strategic policy inputs to enhance economic growth through:- Encouraging industrial growth via the PLI scheme.
- Supporting start-ups and innovation through AIM.
- Promoting sustainability and renewable energy adoption.
- Q7: What are NITI Aayog’s goals for 2030?
A: Key goals for 2030 include:- 50% of India’s energy to come from renewable sources.
- Achieving 500 GW non-fossil energy capacity.
- Reducing carbon emissions by one billion tonnes.
- Enhancing public health surveillance systems.
- Achieving major Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Q8: What is NITI Aayog’s vision for 2035?
A: By 2035, NITI Aayog envisions:- Sustained economic growth with a balance of social equity.
- Energy security with affordable and accessible power.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration in key sectors like healthcare, education, and urban planning.
Conclusion
Marking a decade of transformative governance, NITI Aayog has been instrumental in shaping India’s developmental narrative. Through policy innovation, cooperative federalism, and data-driven strategies, it has addressed pressing challenges while setting ambitious goals for the future.
As it continues to redefine India’s governance framework, NITI Aayog’s role will be crucial in steering the country toward sustainable, inclusive, and equitable growth.
Key Takeaways Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Established | January 1, 2015, replacing the Planning Commission. |
| Key Objective | Promoting decentralized governance, innovation, and inclusive growth. |
| Governance Approach | Emphasizes cooperative and competitive federalism. |
| Major Programs | Aspirational Districts Program (ADP), Atal Innovation Mission (AIM), Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, SDG India Index, Aspirational Blocks Program (ABP). |
| Impact on Economy | Boosted manufacturing, start-ups, and data-driven policy-making. |
| Goals for 2030 | Renewable energy expansion, skill development, and poverty reduction. |
| Vision for 2035 | Focus on AI integration, sustainability, and economic equity. |
SEO-Driven Tags
- NITI Aayog 10-Year Achievements
- Aspirational Districts Program Impact
- Atal Innovation Mission Success
- NITI Aayog’s Role in Indian Economy
- Sustainable Development Goals India
- Production Linked Incentive Scheme 2025
- India’s Governance Reforms 2024





