SEBI’s Measures to Curb Speculative Trading in Index Derivatives
Introduction: Why These Measures Matter
In recent times, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has observed a surge in speculative trading in index derivatives, resembling gambling behavior. To safeguard financial markets and investors, SEBI has proposed several measures to curb excessive speculation. Understanding these changes is crucial for traders and competitive exam aspirants as they reflect evolving market regulations and economic policies.
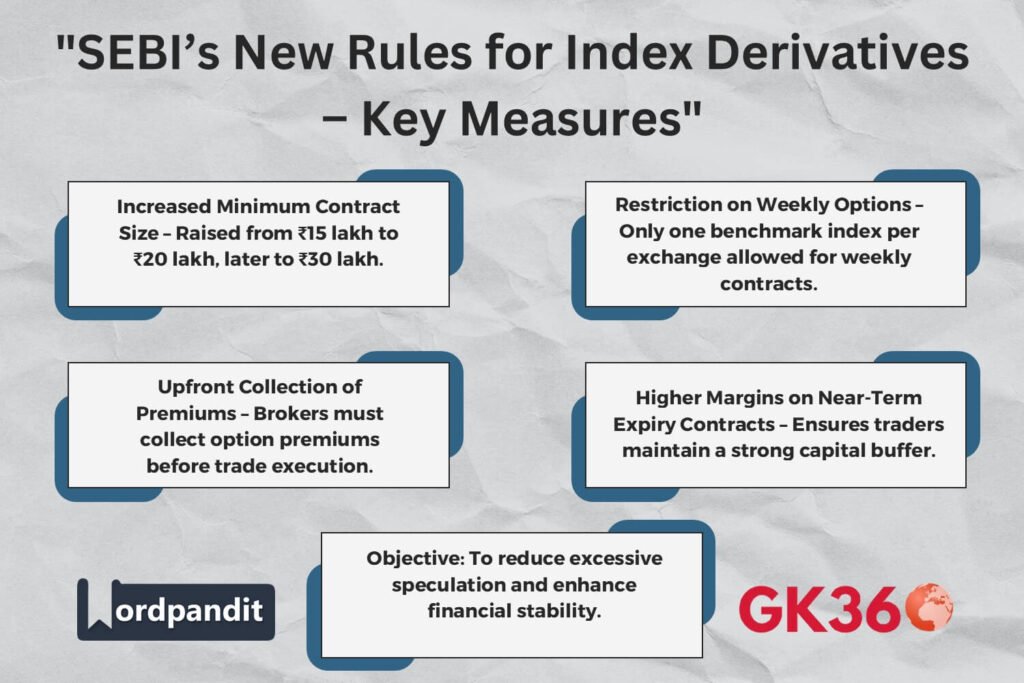
Table of Contents
- Introduction: Why These Measures Matter
- Key Measures Proposed by SEBI
- Understanding Futures and Options
- About SEBI
- Practical Implications and Preparation Tips
- Conclusion: Embrace the Changes
Key Measures Proposed by SEBI
1. Revising Minimum Contract Size for Index Derivatives
SEBI has proposed a phased increase in the minimum contract size for index derivatives:
- Phase 1: Minimum value of a derivatives contract at the time of introduction: ₹15 lakhs to ₹20 lakhs
- Phase 2: After six months, the minimum value increases to ₹20 lakhs to ₹30 lakhs
Objective: This change aims to limit speculative trading by ensuring only traders with sufficient capital participate.
2. Weekly Options Contracts on a Single Benchmark Index
- SEBI proposes restricting weekly options contracts to a single benchmark index per exchange.
Objective: This will reduce market complexity and limit speculative trading opportunities.
3. Upfront Collection of Option Premiums
- Brokerages will be required to collect option premiums on an upfront basis from clients.
Objective: Ensures traders have the necessary funds to cover potential losses, reducing the risk of default.
4. Increasing Margins on Near-Term Expiry Contracts
- SEBI proposes increasing margins on near-term expiry contracts.
Objective: This will require traders to maintain a larger buffer against potential losses, discouraging excessive speculation.
Understanding Futures and Options
Futures Contracts
Definition: A standardized agreement to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a future date.
Purpose: Used for hedging risks, speculating on price movements, and gaining leverage.
Options Contracts
Definition: Gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an asset at a specified price before or on a specified date.
Types of Options:
- Call Option: Right to buy an asset.
- Put Option: Right to sell an asset.
About SEBI
- Establishment: Founded on 12 April 1988, gained statutory powers on 30 January 1992 through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- Headquarters: Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- Chairman: Madhabi Puri Buch (first woman to lead SEBI).
- Role: Regulates securities and commodity markets in India under the Ministry of Finance.
Practical Implications and Preparation Tips
For Competitive Exam Aspirants
- Stay Updated: Follow SEBI updates and financial news to track regulatory changes.
- Understand Core Concepts: Learn the fundamentals of futures and options trading.
- Real-Life Applications: Relate theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, such as how increased contract sizes impact market volatility.
- Practice Questions: Solve past exam questions related to financial markets and SEBI regulations.
- Mock Tests: Take finance and derivatives-related mock tests to improve exam readiness.
Encouragement for Self-Exploration
- Explore Further: Visit SEBI’s official website for more details on regulations.
- Join Forums: Participate in finance and trading forums for discussions on market trends.
- Read Books: Reference books like Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives by John C. Hull for deeper insights.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is SEBI increasing the minimum contract size for index derivatives?
SEBI aims to limit speculative trading by ensuring that only traders with sufficient capital participate in the market.
2. How will restricting weekly options contracts affect traders?
This move simplifies the market structure and reduces speculative trading opportunities, promoting stability.
3. What is the impact of upfront option premium collection?
It ensures that traders have the necessary funds to cover potential losses, reducing default risks.
4. How do higher margins on near-term expiry contracts help?
Higher margins create a financial buffer, discouraging excessive speculation and improving market stability.
5. Where can I learn more about SEBI’s regulations?
You can visit SEBI’s official website or refer to financial news sources for updates on regulatory changes.
Conclusion: Embrace the Changes
Understanding and adapting to SEBI’s proposed measures is essential for staying ahead in both competitive exams and finance. These regulations aim to create a more stable and secure financial environment. By keeping yourself informed and refining your knowledge, you enhance your ability to navigate the evolving financial landscape with confidence.
Every change in financial regulation presents an opportunity to learn and grow. Stay motivated, keep exploring, and success will follow.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Regulator | Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) |
| Objective | Reduce excessive speculation in index derivatives |
| Minimum Contract Size | Increased from ₹15 lakh to ₹30 lakh (phased approach) |
| Weekly Options Restriction | Only one benchmark index per exchange for weekly contracts |
| Premium Collection Rule | Brokers must collect upfront option premiums before execution |
| Margin Rules | Higher margins for near-term expiry contracts to reduce volatility |
| Impact on Traders | Encourages long-term, well-capitalized investments |
Relative Terms
- SEBI New Trading Rules 2025
- Index Derivatives Regulations India
- SEBI Futures and Options Market Changes
- SEBI Minimum Contract Size 2025
- Weekly Options Restrictions SEBI
- SEBI Trading Margin Rules Explained
- Futures vs. Options Trading India
- Understanding Index Derivatives Trading
- Indian Stock Market Regulations Update
- SEBI Measures Against Speculative Trading





