International Day of Zero Tolerance for FGM 2025: Global Action to End Female Genital Mutilation
Introduction
The International Day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation (FGM), observed annually on February 6, raises awareness about the urgent need to eliminate this harmful practice. FGM is a severe violation of human rights, with devastating physical, psychological, and social consequences for millions of women and girls worldwide.
While concentrated in 30 countries across Africa and the Middle East, FGM is a global issue, with cases reported in Asia, Latin America, and among immigrant communities in Europe, North America, and Australia. To meet the United Nations’ 2030 target of eradicating FGM, global efforts must be accelerated and strengthened.
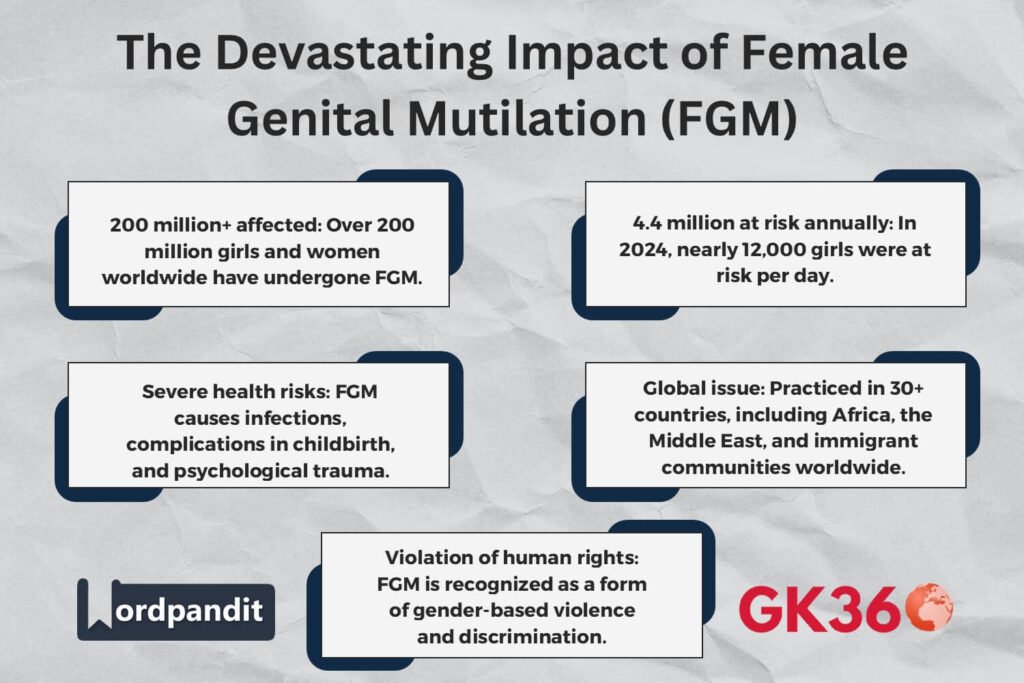
Table of Contents
- Theme for 2025: Step Up the Pace
- The Global Prevalence of FGM
- The Impact of Humanitarian Crises on FGM
- The Consequences of FGM
- Strategies to Eliminate FGM
- Observing the International Day of Zero Tolerance for FGM
- Strengthening Global Commitments
- FAQs About FGM and Global Efforts
- Conclusion: The Road to 2030
Theme for 2025: Step Up the Pace
The 2025 theme, “Step Up the Pace: Strengthening Alliances and Building Movements to End FGM,” highlights the need for collaborative, large-scale interventions to accelerate change. Achieving the global eradication target by 2030 requires:
- Stronger partnerships between governments, NGOs, and local communities.
- Increased funding for education and healthcare services.
- Addressing root causes like gender inequality and harmful social norms.
This theme underscores the need for grassroots mobilization and international policy changes to dismantle FGM practices permanently.
The Global Prevalence of FGM
Current Statistics and Trends
- Over 200 million girls and women worldwide have undergone FGM.
- In 2024 alone, nearly 4.4 million girls were at risk—an average of 12,000 per day.
- While FGM rates have declined by one-third in 30 years, progress remains uneven, particularly in regions affected by poverty, conflict, and displacement.
The Impact of Humanitarian Crises on FGM
Wars, displacement, and natural disasters significantly increase the risk of FGM. In refugee camps and conflict zones, families may turn to FGM under social or economic pressure, seeing it as a means of preserving cultural identity or securing marriage prospects.
Key Risk Factors:
- Breakdown of protective systems: Weak enforcement of anti-FGM laws in crisis-affected areas.
- Economic hardships: Families may resort to FGM due to traditional dowry practices.
- Limited education and healthcare access: Girls in fragile communities have less awareness and protection against FGM.
Urgent humanitarian interventions are essential to prevent FGM during emergencies.
The Consequences of FGM
FGM has lifelong consequences, affecting both physical and mental well-being.
Short-Term Complications
- Severe pain and psychological trauma.
- Excessive bleeding (hemorrhage).
- Life-threatening infections, including sepsis.
- Urinary complications and difficulty urinating.
Long-Term Consequences
- Chronic pain and permanent scarring.
- Obstetric complications (higher risk of stillbirths, maternal deaths).
- Increased risk of HIV/AIDS and reproductive infections.
- Psychological distress (PTSD, anxiety, depression).
- Sexual dysfunction and infertility.
Beyond health impacts, FGM reinforces gender discrimination and limits women’s autonomy, violating fundamental human rights.
Strategies to Eliminate FGM
The Role of Education and Advocacy
Promoting Gender Equality and Human Rights
- Incorporating FGM education into school curricula to empower young girls.
- Engaging men and boys as allies in challenging harmful gender norms.
- Creating safe spaces for survivors to share experiences and access support.
By framing FGM as a human rights violation, global advocacy efforts can push for stronger laws and policies.
The Power of Media and Technology
Social Media Campaigns
- Movements like #EndFGM and #Unite2EndFGM amplify survivor voices and mobilize action.
- Influencers and activists use digital platforms to reach millions worldwide.
Mobile Apps and Helplines
- Apps provide anonymous access to information, legal support, and emergency help.
- Helplines offer 24/7 crisis intervention for at-risk girls.
Technology bridges gaps in accessibility and ensures immediate protection for vulnerable communities.
Observing the International Day of Zero Tolerance for FGM
Declared by the UN General Assembly in 2012, this annual observance is a call to action. Activities include:
- Global conferences and policy discussions.
- Survivor-led storytelling events.
- Fundraising initiatives supporting anti-FGM programs.
Strengthening Global Commitments
Key Actions Needed:
- Enforcing stronger laws against FGM, with harsher penalties.
- Expanding healthcare services for victims and at-risk girls.
- Engaging communities in social change efforts to reject FGM permanently.
Governments, civil society, and global organizations must work together to ensure FGM is eradicated by 2030.
FAQs About FGM and Global Efforts
1. What is Female Genital Mutilation (FGM)?
FGM involves the partial or complete removal of external female genitalia for non-medical reasons, violating human rights.
2. Where is FGM most prevalent?
Primarily in 30 African and Middle Eastern countries, but also in parts of Asia, Latin America, and Western immigrant communities.
3. How is the UN fighting against FGM?
Through the UNFPA-UNICEF Joint Programme, awareness campaigns, and legal reforms.
4. How can individuals help end FGM?
Support organizations like UNICEF, WHO, and local NGOs.
Educate others about the dangers of FGM.
Advocate for stronger policies and community programs.
Conclusion: The Road to 2030
The International Day of Zero Tolerance for FGM 2025 serves as a global call for action. While progress has been made, FGM still threatens millions of girls. By strengthening partnerships, investing in education, and amplifying survivor voices, the world can end FGM by 2030.
Ending FGM means empowering women and girls, protecting their rights, and ensuring a future free from gender-based violence.
Key Takeaways
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| 2025 Theme | “Step Up the Pace: Strengthening Alliances and Building Movements to End FGM” |
| Global Prevalence | 200 million+ affected worldwide, with 4.4 million at risk in 2024 alone. |
| Impact of Crises | Wars, displacement, and poverty increase FGM risks, especially in refugee communities. |
| Health Consequences | Includes severe pain, infections, childbirth complications, and psychological trauma. |
| Eradication Strategies | Survivor-led activism, stronger laws, education, and community engagement. |
| Role of Technology | Social media campaigns, mobile apps, and helplines provide education and emergency support. |
| Global Commitment | UN’s 2030 goal aims for complete eradication through coordinated international efforts. |
Related Terms:
- End FGM 2025
- Female Genital Mutilation Awareness
- Zero Tolerance for FGM
- UN FGM Eradication Goals
- Stop Gender-Based Violence
- FGM Health Consequences
- Survivor-Led FGM Activism
- Global Human Rights Campaigns
- February 6 UN Observance
- FGM Prevention and Education






