India’s Nuclear Energy Growth: A Decade of Expansion & Future Projections
Introduction
India has made significant strides in nuclear power generation over the past decade, doubling its atomic power capacity from 4,780 MW in 2014 to 8,081 MW in 2024. This rapid expansion, achieved within just ten years, contrasts sharply with the six decades it previously took to reach similar milestones. With ambitious plans to triple the nuclear power capacity to 22,480 MW by 2031-32, India is positioning itself as a major global player in sustainable and secure energy production. This article explores India’s nuclear energy growth, key milestones, challenges, and future projections.
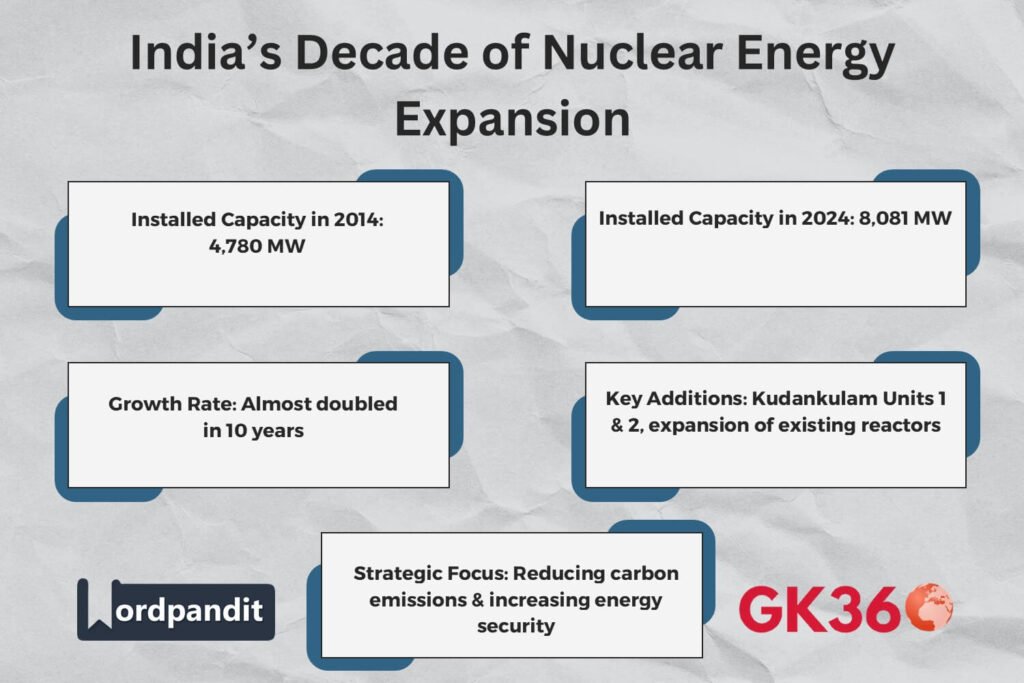
Table of Contents
- India’s Atomic Power Growth (2014-2024)
- Future Projections for 2031-32
- Role of Political Leadership and Technological Advancements
- Challenges in India’s Nuclear Power Expansion
- India’s Nuclear Power vs. Global Leaders
- Peaceful Applications of Nuclear Energy
- Thorium Reserves & Sustainability: India’s Unique Advantage
- FAQs on India’s Nuclear Energy Growth
- Conclusion: The Road Ahead for India’s Atomic Power
India’s Atomic Power Growth (2014-2024)
India’s nuclear energy capacity has grown significantly in the last decade. In 2014, the country had an installed nuclear power capacity of 4,780 MW, which has now expanded to 8,081 MW in 2024. The rapid growth is due to several factors:
- Commissioning of new nuclear power plants such as Kudankulam Units 1 and 2
- Expansion of existing facilities with advanced reactor technology
- Strong government support through policies promoting nuclear energy
With a focus on reducing carbon emissions and achieving energy security, nuclear power has become a cornerstone of India’s energy strategy.
Future Projections for 2031-32
India aims to triple its nuclear power capacity to 22,480 MW by 2031-32. Several projects are in the pipeline to achieve this goal:
- Construction of additional Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs)
- Fast-tracking of Light Water Reactor (LWR) projects in collaboration with international partners
- Expansion of existing nuclear sites with next-generation technologies
Role of Political Leadership and Technological Advancements
A conducive political environment has played a vital role in India’s nuclear energy expansion. Policy reforms, increased investment, and international collaborations have fueled growth. Technological advancements include:
- Development of advanced fuel cycles to improve efficiency
- Enhanced safety mechanisms for nuclear reactors
- Increased research on small modular reactors (SMRs)
Challenges in India’s Nuclear Power Expansion
Despite rapid progress, India faces several challenges in its nuclear energy journey:
- Infrastructure Limitations: Delays in reactor construction due to land acquisition and environmental approvals
- Financial Constraints: High capital costs and funding challenges
- Regulatory & Safety Concerns: Stringent regulatory processes can slow down project execution
India’s Nuclear Power vs. Global Leaders
India is gradually positioning itself among global nuclear leaders. A comparative analysis:
- United States (95,000+ MW): Heavy reliance on nuclear energy with a well-established reactor fleet
- Russia (39,000+ MW): Strong emphasis on export-led nuclear technology
- China (53,000+ MW): Rapidly expanding nuclear sector with government-backed investments
- France (61,000+ MW): Among the highest shares of nuclear power in total electricity generation
While India lags behind in overall installed capacity, it has the potential to become a major player through indigenous innovation and strategic collaborations.
Peaceful Applications of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy in India is not limited to power generation; it is also revolutionizing various sectors:
- Agriculture: Development of 70+ radiation-mutated crop varieties, improving food security
- Healthcare: Use of nuclear isotopes in cancer treatments and diagnostic imaging
- Industry: Applications in material testing and preservation technologies
Thorium Reserves & Sustainability: India’s Unique Advantage
India possesses 21% of the world’s thorium reserves, making it a global leader in thorium-based nuclear energy research. Future sustainability efforts include:
- Development of thorium-fueled Advanced Heavy Water Reactors (AHWRs)
- Reducing dependence on imported uranium
- Enhancing long-term energy security through indigenous fuel sources
FAQs on India’s Nuclear Energy Growth
Q1: How does nuclear power contribute to India’s energy security?
A1: It provides a stable, low-carbon energy source, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Q2: What are the benefits of thorium-based reactors?
A2: Thorium reactors produce less nuclear waste and have enhanced safety features.
Q3: What steps is India taking to ensure nuclear safety?
A3: Implementation of advanced safety mechanisms and adherence to IAEA guidelines.
Q4: How does India’s nuclear power compare with China’s?
A4: While China has a larger nuclear capacity, India focuses on sustainable thorium-based energy.
Q5: What future collaborations are planned for nuclear energy development?
A5: India is working with Russia, the US, and France on advanced reactor technologies.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead for India’s Atomic Power
India’s nuclear power sector has seen remarkable growth from 4,780 MW in 2014 to 8,081 MW in 2024, with plans to reach 22,480 MW by 2031-32. With government backing, technological advancements, and strategic partnerships, India is set to become a major player in global nuclear energy. By leveraging its thorium reserves and ensuring sustainable growth, the nation is paving the way for a secure, low-carbon energy future.
Key Takeaways Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Nuclear Capacity Growth (2014-2024) | 4,780 MW to 8,081 MW, nearly doubling in a decade. |
| Target for 2031-32 | 22,480 MW nuclear power capacity. |
| Government Strategies | Expansion of PHWRs, LWRs, and Thorium-based reactors. |
| Global Standing in Nuclear Energy | Competing with China (53,000+ MW), France (61,000+ MW), and the US (95,000+ MW). |
| Challenges Ahead | Infrastructure constraints, high costs, regulatory approvals. |
| Thorium-Based Reactors | India is a global leader in thorium research, ensuring long-term sustainability. |
Related Terms:
- India nuclear energy expansion
- India nuclear power growth 2024
- India nuclear targets 2031
- India thorium-based reactors
- India vs China nuclear energy comparison
- India’s role in global nuclear energy
- Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) India
- India’s energy security and nuclear power
- Future of nuclear power in India
- India’s clean energy initiatives






