India’s Immigration and Foreigners Bill 2025: Key Reforms, Impact & National Security
Introduction
In a landmark move to modernize India’s immigration system, the Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025, has been introduced in the Indian Parliament by the Minister of State for Home Affairs, Nityanand Rai. This proposed legislation aims to replace outdated colonial-era immigration laws, enhance national security, and streamline the legal framework for foreign nationals in India.
By consolidating multiple immigration regulations into a single, structured legal framework, the bill seeks to simplify enforcement, increase accountability, and establish a more transparent immigration process that aligns with India’s evolving global role.

“Infographic summarizing major reforms in India’s new immigration law, focusing on security, registration, penalties, and enforcement.”
Table of Contents
- Why India Needs Immigration Reform
- Colonial-Era Laws Set for Repeal
- Key Provisions of the Immigration and Foreigners Bill 2025
- Impact on National Security & Foreign Visitors
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion & Future Outlook
Why India Needs Immigration Reform
India’s immigration framework has long been governed by four separate acts, some dating back to the British colonial era. Overlapping regulations have led to legal ambiguities, inefficient enforcement, and difficulty in tracking foreign nationals.
Key Issues with Existing Laws:
- Outdated Provisions: Some laws were designed before India’s independence.
- Lack of Cohesion: Separate laws for entry, visa, and penalties create confusion.
- Weak Security Provisions: Existing penalties are insufficient to deter illegal immigration.
With India becoming a global business hub and a popular destination for international visitors, the government has sought a modern, consolidated framework to streamline immigration management.
Colonial-Era Laws Set for Repeal
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 will replace four existing acts:
- The Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920
- The Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939
- The Foreigners Act, 1946
- The Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000
These acts have been criticized for being fragmented and inconsistent in defining foreigner registration, visa rules, and penalties. The new bill unifies all these aspects into a single, structured framework.
Key Provisions of the Immigration and Foreigners Bill 2025
Entry Restrictions for Foreigners
- Foreign nationals deemed a threat to national security, sovereignty, or public order can be denied entry or deported.
- Border authorities will have clear guidelines to identify and restrict entry based on intelligence alerts.
Mandatory Registration and Movement Regulations
- Every foreigner entering India must register with immigration authorities.
- Restricted zones, including border areas and strategic regions, will have stricter entry controls for foreign nationals.
- Educational institutions, hospitals, and employers must report the presence of foreign nationals under their authority.
Stricter Penalties for Violations
- Illegal entry → Up to 5 years imprisonment + ₹5 lakh fine.
- Using fraudulent documents → 2 to 7 years imprisonment + ₹1-10 lakh fine.
- Overstaying visas → 3 years imprisonment + ₹3 lakh fine.
- Entering restricted zones → Immediate detention and deportation.
Transport Carrier Liabilities
- Airlines, shipping companies, and other carriers must verify passengers’ immigration documents before travel.
- Failure to comply can lead to:
- ₹5 lakh fine per passenger
- Seizure of the transport vehicle if non-compliance persists
Enhanced Powers for Immigration Officers
- Officers can arrest foreign nationals without a warrant if immigration laws are violated.
- They can restrict a foreigner’s internal movement in India.
- Authorities may deny departure if a person is linked to national security concerns.
Advance Passenger Data Sharing
- Airlines must share passenger details before arrival to enable early threat detection.
- This data-sharing strengthens border security and reduces immigration fraud risks.
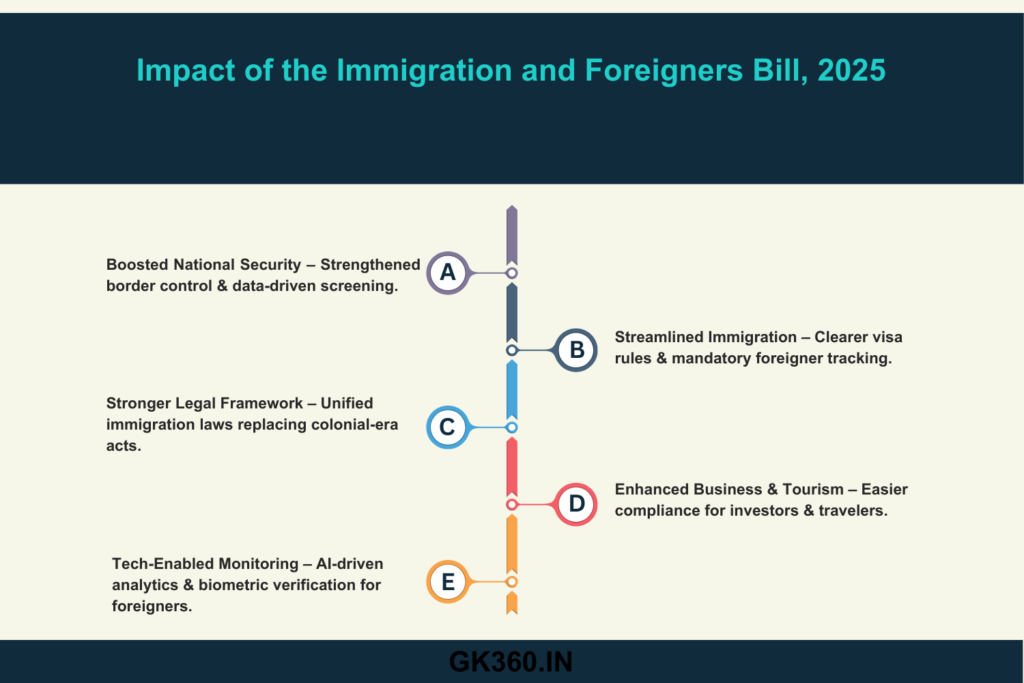
Impact on National Security & Foreign Visitors
- Boosted National Security:
- Stronger border control measures will help prevent illegal immigration and espionage risks.
- Advanced screening will block entry for individuals flagged as security threats.
- Streamlined Immigration for Legal Visitors:
- Clearer visa guidelines make the process simpler and more transparent.
- Mandatory registration ensures better tracking of foreign nationals, reducing overstay violations.
- Enhanced Trade & Tourism:
- A well-defined immigration framework will boost investor confidence.
- Faster clearance processes will benefit genuine tourists, students, and professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025?
It is a new immigration law proposed to replace outdated colonial-era acts, streamline foreigner registration, and improve national security.
- What happens if a foreigner overstays their visa?
The new law proposes up to 3 years of imprisonment and a fine of ₹3 lakh.
- How will transport carriers be affected?
Airlines and shipping companies must verify documents before transport. Non-compliance may result in hefty fines or vehicle seizure.
- Does this law affect Indian citizens?
No, this law applies only to foreign nationals. However, Indian authorities handling foreign visitors will have more responsibility.
- How will this impact tourism and business travel?
While security checks will increase, the bill aims to simplify processes for genuine travelers and business professionals.
“Infographic detailing the national security, business, and technological impacts of India’s new immigration law.”
Conclusion & Future Outlook
The Immigration and Foreigners Bill, 2025 represents a major transformation in India’s immigration landscape. By replacing four outdated colonial-era laws, the bill brings clarity, accountability, and efficiency to the management of foreign nationals in India. The new registration system, stricter penalties, and enhanced enforcement measures are expected to bolster national security and streamline immigration processes.
Additionally, this legislation positions India as a leader in modern immigration policies by integrating cutting-edge technologies such as biometric verification, real-time data tracking, and AI-driven security analytics to monitor foreign arrivals and departures efficiently.
However, challenges remain in ensuring seamless implementation, including training immigration officers, modernizing border control infrastructure, and integrating databases for real-time intelligence sharing. Addressing these aspects will be crucial in ensuring the bill’s effectiveness.
Key Takeaways Table
| Aspect | Details |
| Purpose of the Bill | Modernizes immigration laws, strengthens national security, and improves tracking of foreign nationals. |
| Laws Replaced | The Passport (Entry into India) Act (1920), The Registration of Foreigners Act (1939), The Foreigners Act (1946), The Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act (2000). |
| Key Provisions | Entry restrictions, mandatory registration, stricter penalties, carrier liabilities, enhanced officer powers, data-sharing mandates. |
| Penalties for Violations | Illegal entry (5 years + ₹5 lakh fine), Overstaying (3 years + ₹3 lakh fine), Document fraud (2–7 years + ₹1–10 lakh fine). |
| Security Enhancements | Real-time passenger screening, biometric tracking, and AI-based monitoring of foreigners. |
| Business & Tourism Impact | Simplified visa rules, faster clearance, and a structured compliance framework. |
| Challenges in Implementation | Need for officer training, infrastructure upgrades, and real-time intelligence integration. |





