Cali Fund at COP16: Transforming Global Biodiversity Finance & Corporate Responsibility
Introduction: The Need for Sustainable Biodiversity Finance
Biodiversity loss is accelerating at an alarming rate, driven by deforestation, climate change, and industrial expansion. Securing sustainable financing mechanisms is crucial to halting and reversing this decline. At the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), a landmark initiative was launched: the Cali Fund. This innovative financial mechanism aims to mobilize corporate contributions toward global biodiversity conservation, ensuring that industries benefiting from genetic resources reinvest in their preservation.

Table of Contents
- What is the Cali Fund? A Game-Changer at COP16
- How the Cali Fund Works: Governance & Industry Contributions
- Role of the Private Sector: Ensuring Corporate Accountability
- The Link Between Genetic Data & Biodiversity Finance
- The Cali Fund & Global Conservation Agreements
- Future Prospects: What’s Next for the Cali Fund?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion & Call to Action
What is the Cali Fund? A Game-Changer at COP16
The Cali Fund, introduced at CBD COP16 in Rome, Italy, is designed to finance global biodiversity conservation efforts by leveraging contributions from industries that utilize genetic resources. By aligning with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF), the fund provides a structured approach to biodiversity finance, ensuring sustainable and equitable resource allocation.
How the Cali Fund Works: Governance & Industry Contributions
Financial Contributions from Industries
Industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, agriculture, and cosmetics, which rely on genetic and biological resources, are required to contribute financially to the Cali Fund. This ensures that businesses benefiting from biodiversity play an active role in its conservation.
Governance Structure
The fund is managed by an international governing body comprising representatives from governments, environmental organizations, scientific communities, and corporate stakeholders. This governance structure guarantees transparency, accountability, and strategic fund allocation.
Investing in Biodiversity Conservation
The financial contributions collected are directed toward biodiversity-rich regions, supporting initiatives such as:
- Habitat restoration
- Endangered species protection
- Sustainable community development
- Scientific research on conservation strategies
Role of the Private Sector: Ensuring Corporate Accountability
The Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing (ABS) emphasizes the equitable distribution of benefits derived from genetic resources. The Cali Fund integrates these principles, holding corporations accountable for the impact of their operations on biodiversity. By linking profits to conservation, businesses are incentivized to adopt sustainable practices.
The Link Between Genetic Data & Biodiversity Finance
Advances in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals heavily depend on genetic resources. Historically, the financial gains from these resources have not been equitably shared, leading to concerns over biopiracy. The Cali Fund ensures that revenues from genetic data utilization are reinvested into conservation, fostering ethical and sustainable biodiversity finance.
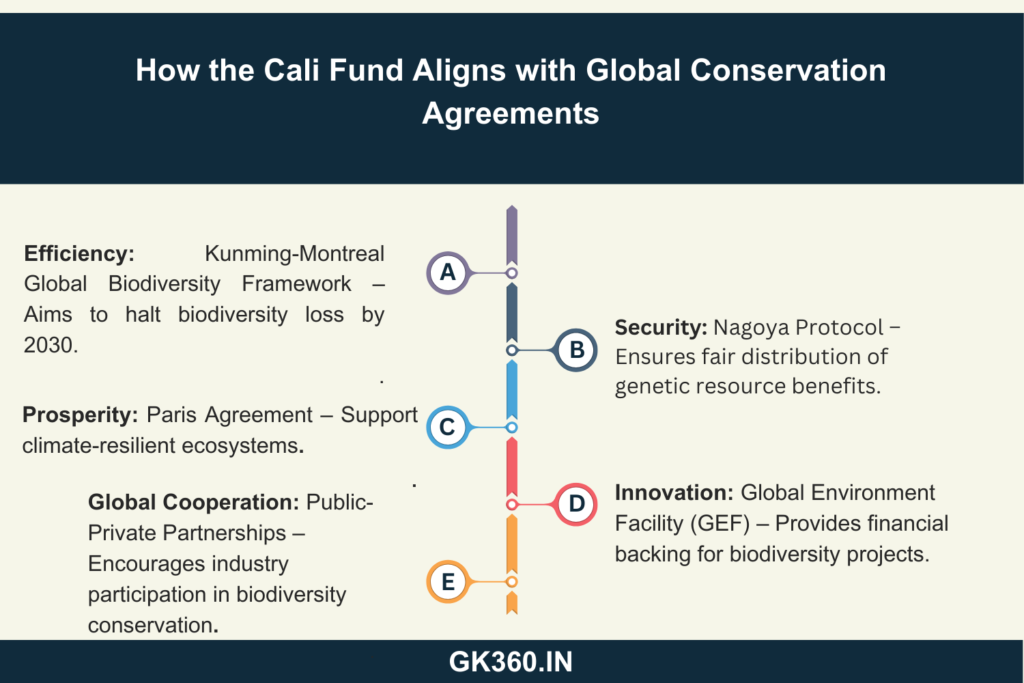
The Cali Fund & Global Conservation Agreements
The fund aligns with several international conservation agreements, including:
- Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) – Goal: Halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030.
- Nagoya Protocol – Ensures fair and equitable benefit sharing.
- Paris Agreement – Supports climate-resilient ecosystems.
- Global Environment Facility (GEF) – Provides financial support for biodiversity projects.
Future Prospects: What’s Next for the Cali Fund?
The success of the Cali Fund depends on global cooperation, corporate participation, and transparent implementation. Future steps include:
- Expanding the fund’s contributors to include more industries.
- Strengthening monitoring systems to track fund utilization.
- Encouraging public-private partnerships to enhance biodiversity finance.
- Integrating innovative funding models, such as carbon credits and biodiversity bonds.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1.What industries contribute to the Cali Fund?
Sectors like pharmaceuticals, agriculture, biotechnology, and cosmetics are mandated to contribute due to their reliance on genetic resources.
How does the Cali Fund align with global biodiversity goals?
It directly supports the KMGBF, which aims to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030 through sustainable financing.
How are the funds distributed?
Funds are allocated based on priority conservation needs, focusing on endangered species protection, habitat restoration, and community-led initiatives.
What measures ensure corporate accountability?
Companies are required to disclose genetic resource utilization data, and non-compliance results in financial penalties and exclusion from biodiversity-related markets.
How can individuals and organizations support the Cali Fund?
Individuals can support through donations, advocacy, and sustainable consumption practices, while organizations can participate in corporate sustainability programs.
Conclusion
The Cali Fund at COP16 represents a pioneering effort in biodiversity finance, ensuring that industries benefiting from genetic resources actively contribute to their preservation. By fostering corporate accountability, global collaboration, and sustainable financing, the fund is poised to play a crucial role in halting biodiversity loss by 2030.
Key Takeaways Table
| Aspect | Details |
| Cali Fund Introduction | Launched at COP16 to finance biodiversity conservation. |
| Industries Involved | Pharmaceuticals, biotech, agriculture, cosmetics contribute to the fund. |
| Governance Structure | Managed by international bodies to ensure fair fund distribution. |
| Corporate Responsibility | Holds companies accountable under the Nagoya Protocol. |
| Fund Allocation | Supports habitat restoration, endangered species protection, and scientific research. |
| Global Conservation Alignment | Works with KMGBF, Paris Agreement, and GEF for biodiversity protection. |
| Future Goals | Expansion to more industries, increased transparency, and biodiversity bonds. |
Related Terms:
- Cali Fund COP16
- Biodiversity Finance
- Global Conservation Agreements
- Corporate Sustainability & Biodiversity
- Nagoya Protocol Compliance
- Kunming-Montreal Biodiversity Framework
- Sustainable Genetic Resource Utilization
- Industries & Biodiversity Conservation
- Public-Private Partnerships in Biodiversity
- Biodiversity Bonds & Finance Models





